
Artificial Insemination
Artificial Insemination

"Artificial insemination is the simplest technique we perform to achieve pregnancy."
Artificial insemination, whether with partner or donor sperm, is the simplest assisted reproduction technique we can perform to achieve pregnancy. It involves introducing selected and activated sperm into the uterus at the exact moment of ovulation to facilitate the fertilization process.
Conjugal Artificial Insemination (IAC) has the following indications:
- Mild ovulatory cycle alterations in women under 40 years old.
- There should be no obstruction in the fallopian tubes.
- Inability to deposit semen in the vagina.
- No severe alterations in the spouse's semen.
- A minimum value in the recovery of motile sperm (REM) in the spermogram is required.
- Cases of infertility of unknown origin.
Artificial Insemination with Donor (IAD) has the following indications:
- Absence of a male partner: Single woman or female partner.
- Genetic diseases in the man whose transmission to offspring cannot be prevented by pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
- Severe male factor: If pregnancy is not achieved after several ICSI cycles and the woman's characteristics are favorable to this technique.
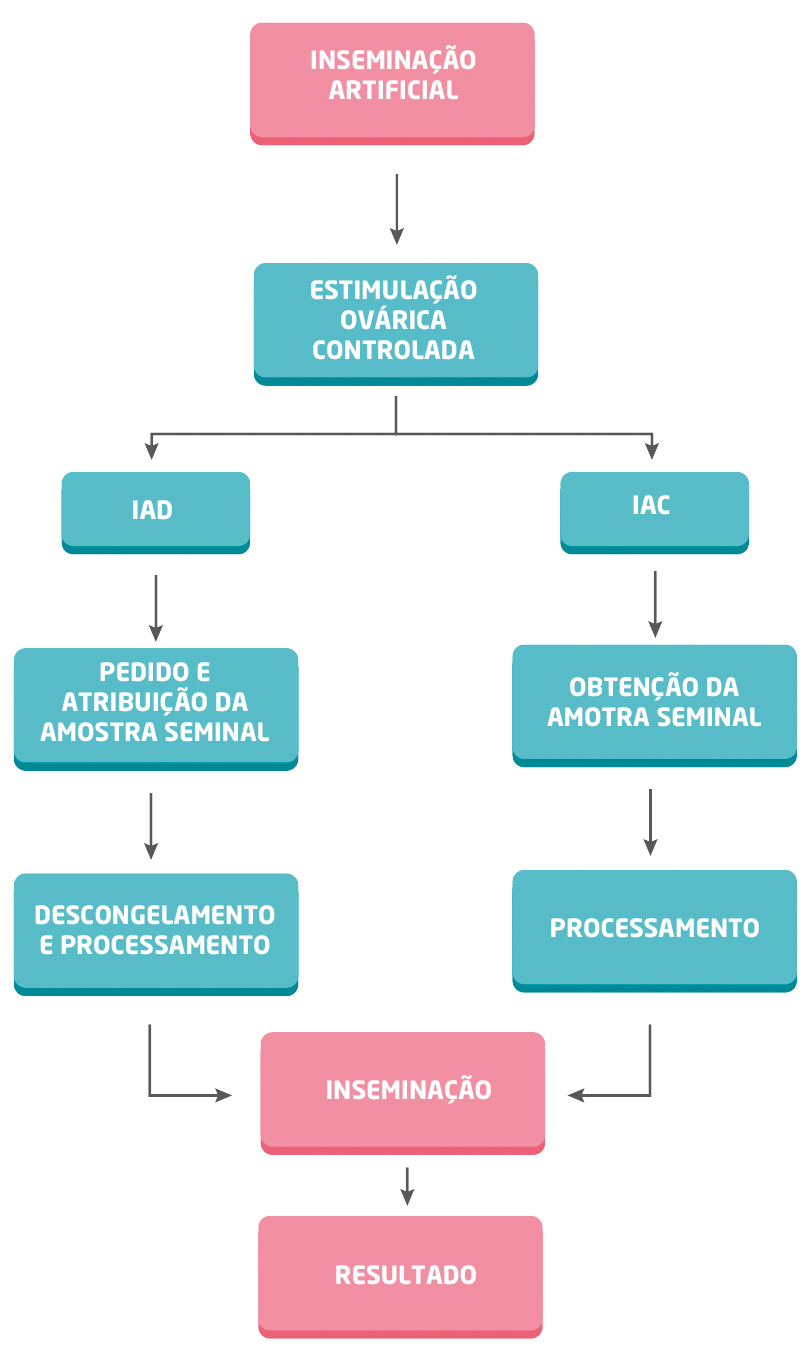 This technique involves the following steps:
This technique involves the following steps:
- Controlled ovarian stimulation: Ovulation coordination involves administering low doses of medication to trigger ovulation.
- Semen capacitation: The man must collect the semen sample at our center's facilities. The laboratory team will then process the sample, facilitating the capacitation process that will activate the sperm for fertilization.
- Insemination: It involves transferring the activated sperm into the uterine cavity through a cervical canalization probe.
This way, the distance between the sperm and the egg is shortened, and their meeting is facilitated.
The process itself is relatively simple, does not require any special intervention, and is performed in the examination room. This process is painless and does not require fasting or special recommendations. Usually, the day after insemination, progesterone treatment is started, and folic acid is also recommended.
Artificial insemination is generally performed with the couple's semen and is called conjugal artificial insemination (IAC). In other cases, such as total absence of sperm (Azoospermia) or in the case of women without a partner, it can be done with donor semen (IAD).
To perform IAC, minimum values in the spermogram are required, especially in the recovery of motile sperm (REM). Additionally, there should be no obstruction in the fallopian tubes. Other factors to consider when indicating the convenience of artificial insemination are the woman's age and previous fertility treatments she has undergone.
Both IAC and IAD require an ovarian stimulation protocol to ensure the proper development of the follicles containing the eggs and to coordinate the timing of insemination with the sperm. For this, medication consisting mainly of injectable hormones must be administered. The doses are low, and the medication is very easy to administer, as it is usually subcutaneous (like insulin in diabetic patients). The growth of the ovarian follicles must be monitored periodically by vaginal ultrasound until they reach an adequate size. This medication and control process lasts approximately 10-12 days. An appointment is scheduled for insemination, and on the scheduled day and time, the couple will come to the clinic. The insemination process itself is relatively simple and does not require any special intervention in the woman and is performed in the examination room. On the same day, a semen sample will be collected and delivered to the laboratory approximately 1 hour in advance. In the case of IAD, the IERA laboratory will provide a semen donor with the specific characteristics requested by the couple (blood type, height, eye color, etc.).
The andrology laboratory prepares the semen sample to recover the most suitable sperm for fertilization (REM), mimicking what occurs physiologically in the fallopian tubes. The sperm are loaded into a catheter for insemination and introduced through the cervix to deposit the sperm in the region closest to the tubes. This process is painless and does not require fasting or special recommendations. After that, there will be 5 minutes of rest, after which the couple can leave the center.
Artificial insemination has a success rate of approximately 15-20% per attempt. The number of inseminations to be performed depends on many factors, but generally, at IERA, we do not recommend more than 2-3 attempts. If pregnancy is not achieved with IA, it is better to try in vitro fertilization as indicated in the patient circuit.




